The central heating system does not always provide high-quality heating of the home. Under such circumstances, additional heating units are used to create a comfortable microclimate in the rooms. Radiators and convectors are often used for such purposes. They come in different types and differ in their operating principles. To understand which heating equipment is more profitable to use in a particular situation, you need to understand the characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of popular devices.
When choosing between a radiator and a convector for heating a home, you need to evaluate the characteristics and advantages of each of them Source i.ytimg.com
Oil radiators
Heating devices radiate heat in different directions, creating a flow of warm air that is directed upward. As a result of this process, rapid heating of the room occurs.
Most often, oil radiators are used as additional heating units. The main way they differ from convector equipment is their large working area. Due to the circulation of hot mineral oil through the circuit, the entire surface of the radiator is heated. Such devices can be placed anywhere in the room (along the walls, under the table). There are also models designed for wall use only.
There is a heating element inside the oil cooler that warms up the oil, then it releases heat to the surrounding area Source gopb.ru
Pros:
- relatively fast heating of the room;
- mobility of the device;
- presence of built-in thermostats;
- simple maintenance;
- affordable price.
Minuses:
- there is a danger of getting burned due to the strong heating of the device, especially if there are small children in the house;
- Leaks may form in low-quality units;
- are used to produce only additional heat.
The oil radiator should not be left unattended - it is not intended for constant operation Source tehno-rating.ru
Heating using a convector
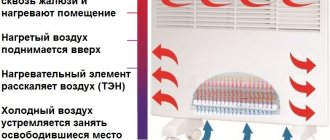
Convector heating is a heating method using more modern types of heaters.
The principle of operation of the convector is different in that it uses natural air circulation to heat the room. Today, the main types of convectors are water and electric.
Water convector.
Their main feature is that they need to be connected to pipes with a coolant - hot water, which heats the air around them. At first glance, they are similar to central heating radiators, however, their main difference is the use of the convection principle for heating.
Radiators use several surfaces (sections) to distribute thermal radiation. For a water convector, this is a pipe on which metal plates are installed. They are heated by the coolant (in this case, hot water) and release heat into the air due to convection.
In addition, the power of convector heating can be controlled by installing control valves, and the heating strength can be adjusted in each room of the house separately.
Advantages of water convectors:
- They heat the room quite efficiently.
- More economical than radiators.
- Silent.
- They do not require electricity.
- They come in different sizes and placement methods (wall-mounted, floor-mounted).
The disadvantages include the complexity of installation - the need to lay a pipe with coolant, as well as the not very fast process of heating the room.
Thus, a water convector is more convenient in comparison with heating radiators in terms of its characteristics, if it is possible to connect pipes with hot water to it.
Electric convector.
This device is the most modern. An electric convector passes cold air through a heating element inside the housing, when heated, it rises, and thus ensures natural circulation of warm air in the room. They are controlled using a thermostat that regulates the temperature.
This type of heater allows you to do without complex installation or pipe laying - you just need to plug it into an outlet, and the device is ready for use.
Advantages of electric convectors:
- When placed correctly, they heat the room efficiently and evenly.
- They do not require complex installation, you only need a nearby outlet.
- Silent.
- Compact, mobile, can be installed on the floor or mounted on the wall. This is why they are better than radiators.
- They can work for a long time without the risk of breakdown.
- Fireproof. Branded models have overheating protection, which turns off the device when tipped over. Also, thanks to the low temperature of the body, you can’t get burned on them, so you don’t have to be afraid to install them in a child’s room.
- You can combine several convectors into a single system, which will make it easier to control the temperature in different rooms.
- Inverter devices with an electric thermostat are quite economical, as they work by maintaining the required temperature.
- Modern models can be controlled via the Internet or mobile devices.
- They have a more affordable price compared to radiators, and you can also save on installation.
The only disadvantage of using an electric convector is the cost of electricity.
However, they can be reduced if you use an inverter type of device. Therefore, today an electric convector is the simplest, most efficient and convenient heating device.
Radiators for water heating
They are used in permanent heating systems (centralized, autonomous). The heating process occurs with the help of a coolant circulating through the circuit. Unlike oil radiators, water radiators do not require power. Connecting a heating system with the latter to a gas boiler significantly reduces the cost of heating a home.
If thermostatic valves are installed on water radiators, it will be possible to set the required temperature in each individual room.
When choosing radiators for water heating, it is extremely important to pay attention to the material they are made from Source kermi.su
Pros:
- huge heat transfer;
- environmental friendliness;
- relatively high power.
Minuses:
- considerable cost;
- excessive heating of the case.
If water radiators are connected to a single heating system, then the temperature in all rooms of the house will be the same Source roomester.ru
Positive and negative characteristics of convectors
Cast iron heating radiator in retro style
Convectors have a lot of positive properties:
- safety;
- more compact shape than all other radiators;
- Possibility of use in combined heating (duplication), when you need to quickly heat a large room;
- high efficiency (superior to other heating devices in efficiency);
- do not require prolonged heating of the case;
- warm (not hot) to the touch, cannot cause burns;
- models built into the floor are better where conventional radiators are inconvenient (panoramic glazing, large hall with a special design concept);
- affordable price.
Built-in models are better where conventional batteries are inconvenient
Forced warm air blowers (with a cooler) have their disadvantages:
- a stream of air raises dust, mold spores and bacterial microflora, which is extremely undesirable for allergy sufferers and asthmatics;
- devices connected on different walls create a draft with a temperature difference (harmful for small children);
- it is necessary to monitor the heat level so that nearby flammable objects and liquids do not overheat;
- uneven heating of the room at one point, especially at the beginning of work;
- difficulties in care. In order for the convector to work for a long time without interruptions, the box and grilles must be regularly and thoroughly cleaned of dust.
Attention! Each variety has its own disadvantages, including energy sources. For large gas boilers, combustion products must be removed under the radiators.
The difference between a convector and a radiator
The difference between a convector and a radiator
Having examined the principles of operation, design features, pros and cons of various devices, you can begin to compare them. It is also worth noting that modern heating units are constantly being improved; new models no longer have significant shortcomings.
The main differences between a convector and a radiator are:
- Compactness. Convector units are more compact and require less space for installation.
- Housing heating rate. Convectors cope with this task faster. But after switching off, they immediately stop heating the room, and the radiators continue to give off heat for some time.
- Safety. The convector body heats up less than the radiator. If you touch the hot surface of the latter, you can get burned.
- Heating of large areas. The radiator copes with this task much more efficiently.
- Easy to maintain. To properly clean a convector unit, it is important to understand how dust gets into it. To clean the radiator, you only need to wash the housing or remove dirt from it.
- Price. It is impossible to unequivocally answer the question which unit (radiator or convector) is more expensive. Due to the significant number of models, there are deviations in different directions.
Plate radiators: accordion radiator options
Introduction
A plate radiator is a bent or straight water pipe with steel plates strung on it. The coolant moves through the pipe, and the plates significantly enhance air convection. The simplicity of the design determines their low price. For aesthetics, the convector is covered with nice boxes made of thin steel, painted white.
Steel plate radiators - general information
Steel plate radiators are commonly called “accordions”. The appearance of an accordion is created by plates strung on a coolant pipe.
A distinctive feature of such radiators is their high reliability. There are no connections in a plate radiator except for the coolant inlet and outlet. As a result, the radiator itself simply cannot leak; there is nowhere for the coolant to break through.
Thanks to the large number of plates and the direct movement of the coolant, the convector heats up to a high temperature. To protect against touches, the main frame of the radiator is covered with a decorative casing. Convection holes are made in the top cover of the casing.
Convectors have low thermal inertia, which means they can be controlled automatically, that is, thermostats can be installed in systems with plate radiators.
Plate radiators form a fairly powerful thermal curtain. This property of convectors allows them to be used in floor heating systems. True, the design of thermal convectors for floor installation differs from wall-mounted convectors, but the heating principle is the same.
Disadvantages of plate radiators (convectors)
- The convective type of radiators does not allow heating the room evenly. Radiators are warmer than the opposite wall of the room.
- The convector plates are an excellent dust collector. They are difficult to clean. Over time, dust reduces their heat transfer.
- The appearance of plate radiators is not encouraging, although there are nice models.
Variations of plate radiators
As options, plate radiators are used for floor heating (duct convectors) and baseboard heating of a room.
Connecting convectors
Two types of convectors are sold by connection
You need to pay attention to this when purchasing. The first type is a convector with side connection
The second type is a convector with a bottom connection0. It is equipped with a valve insert.
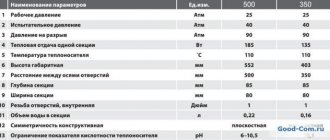
Thermal power of plate radiators
The heat transfer of convectors depends on their length and the number of rows with plates. The height of all convectors is 200 mm.
Thus, the heat transfer of a convector into “one thread” 600 mm long is 347 W. It is 3000 m long and gives a heat output of 1730 W. A radiator with four “threads” 3000 mm long gives a heat output of 4179 W, and one with a length of 1000 mm will give off 1393 W of heat.
The radiator is calculated according to the standard scheme for calculating radiator sections, taking into account all correction factors. Let me remind you how this is done. (read article: Simplified calculation of the heating system)
- For 1 sq. meter of area with a ceiling of 3 meters, you need 100 W of heat.
- For a room of 16 sq. meters, you need a 1600 W radiator. This is under ideal conditions: one window, 3-meter ceiling, the room is not corner. If this is not the case, we apply correction factors:
- Two windows k=1.8: 1600×1.8=2880W;
- Corner room k=1.8: 2880×1.8=5184W;
- Ceiling 2.65, k=2.65/3.0=0.88: 5148W×0.88=4547 W;
- Plastic window k=0.8: 4547W×3637W.
A standard window has a width of 1400 mm, which means that under each window you need to install 4-section plate radiators 1400 mm long, with a heat output of 1950 W. The data is taken from the passports of Purmo radiators. That's all!
What to choose: radiator or convector?
The choice of a heating device largely depends on the conditions of its use, the characteristics of the room, and financial capabilities. Numerous reviews about the use of different radiators and convectors indicate that the latter option is more profitable to buy. Among its positive aspects, they often note: efficiency, significant heat transfer, elegant design, and the ability to heat large rooms. But in order to make a final conclusion, it is worth carefully considering all the pros and cons of individual units.
Typically, convectors are more expensive than radiators. That's why many people prefer the latter. In fact, this is not always beneficial. Convector units have a number of undeniable advantages; their purchase is optimal for most cases.
Environmental friendliness
When asking a question in a store about the difference between a convector and an electric radiator, the buyer may hear a version about burning oxygen. It should be noted that both presented types of heaters are completely identical in terms of environmental characteristics. They do not burn oxygen, contrary to popular belief. There are no combustion processes in them.
If heating elements are heated, oxygen cannot be burned according to existing physical laws. But both presented types of devices will raise dust. This occurs due to the process of convection. When heated air rises, the flow also picks up small light particles. When the air cools, they settle on interior items. Therefore, in terms of microclimate characteristics and environmental parameters, radiators and convectors are on the same level.
Advantages and disadvantages
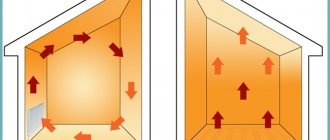
The principle of natural convection is optimal for heating spacious rooms of complex design: with bay windows, arches and partitions. This is due to the following advantages of such an air exchange system:
- fast heating compared to radiator batteries,
- low coolant temperature, which reduces heating costs and reduces the likelihood of burns,
- compactness and light weight.
But the high speed of movement of air volumes leads to the following inconveniences:
- intensive circulation of dust in the room,
- the appearance of drafts due to uneven heating,
- in high rooms heat is used irrationally,
- in convectors with forced ventilation, already heated air is taken in and heated, which reduces efficiency,
- With intense heat exchange, the air becomes very dry, which has an adverse effect on well-being.
Do not forget about one more danger of combining metals in convectors: contact of copper and aluminum in the presence of stray currents in the heating system will lead to the formation of a galvanic couple and rapid corrosion destruction.
As follows from the above characteristics, convectors are optimally used in non-residential premises and private homes.
Compared to cast iron and steel radiators, convectors have obvious advantages. But their shortcomings when choosing between them and aluminum and bimetallic radiators, with comparable prices and almost half the service life, allow us to give the palm to the latter.
Safety first
The types of devices being compared are classified as high-risk heating devices. The devices are equipped with built-in overheating protection. When the maximum temperature is reached, the device automatically turns off.
Electrical devices have an increased risk of electric shock. To prevent injury, it is necessary to strictly comply with fire and electrical safety requirements.
Some models are used in rooms with high humidity. To protect against damage, the devices have a high degree of sealing.
Convector and oil heater comparison reveals the undoubted leader
So, let's compare the main indicators of the two most popular heaters.
1. Economical use. An oil radiator consumes a quarter more electricity than a convector radiator. Since electricity tariffs are constantly rising, this fact may be decisive when choosing a device.
2. Warm-up time. Heating the air with an oil heater goes through several stages: first, electricity heats the heating element, then the heating element heats the oil, and it, in turn, heats the fins of the housing, which gives off heat to the air masses. This takes a lot of time (and costs a lot of electricity) - the device has been turned on for a long time, and the cold is still in the room. Fans built into the oil heater can speed up the process.
In a convector, the heating element immediately heats the body, so its efficiency is at least 95 percent. But the heating rate is also not so high and an oil radiator equipped with a fan, all other things being equal, is more likely to outperform a convector.
3. Comfort during work. This refers to ease of carrying and installation. It should be noted that convectors are more convenient and mobile in this regard. Their weight is no more than 10 kilograms, and oil devices are more bulky and heavy - their weight ranges from 18 to 25 kilograms. Convectors on wheels are more convenient to move, and they are easy to mount on the wall, which will save space in the apartment and make cleaning easier. In addition, the temperature created by the convector is more comfortable. It has no differences throughout the entire volume of the room.
4. Security. You understand that hot oil is not the best neighbor. It heats up the heater body so much that it’s not far from a burn. The exception is heaters equipped with a protective casing.
But convector devices can be called absolutely safe. After all, their body heats up to only 60 degrees, and at this temperature you cannot get burned. Equipped with a protection function, a convector left unattended will not cause any harm to the owner. But under no circumstances should an oil device be left alone with the room - after all, some of its models do not even have an overheating sensor.
5. Service life. Probably more than one person has witnessed oil leaking from an oil heater. Sooner or later a leak appears. First, a microcrack appears on the body, then oil begins to slowly evaporate through it. Well, in the end the heater fails, and no one undertakes to repair it - is it possible to find a tiny microcrack. As for convector heaters, they last for 10 and 15 years, although the manufacturer usually specifies a warranty period of 5 years.
6. Environmental friendliness of the device. To begin with, let’s take it as an axiom that dust in a room will always rise when air moves during convection. Therefore, traders lie when they talk about some special models of convection or oil heaters that do not raise dust. Now about the combustion of oxygen. In convectors, the peculiarity of the heating element material and the heating temperature of the housing are such that this process is physically impossible. Some argue that oxygen combustion is still possible with oil radiators. Don't believe it - it's not true.
7. Cost of the device. Here, oil heaters take the lead - their prices are significantly lower than for convectors. But do not forget about the ratio of price and quality, that is, compare not only prices, but also the most important technical indicators (discussed above).