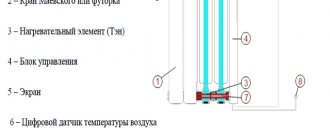
Three types of shut-off and control valves can be used on radiators - shut-off, tuning and regulating a specific device. But why can’t you reduce the cost and use one of the cheapest ball valves, or not use them at all…. How and why the piping is done, which taps to choose correctly for radiators so that the heating system works stably and for a long time...
Ball valves for shut-off
At a minimum, ball shut-off valves should be installed on radiators so that the device can be repaired without draining/stopping the heating system in winter. But ball valves cannot be used for adjustment. If only because it is not possible to make precise adjustments - at 7% of the rotation angle of 90 degrees there is an adjustment range of 85% of the flow.
The valve should not be in intermediate positions at all, since it is worn out by very quickly moving abrasive, cavitation bubbles, and pressing with a piece of wood also occurs, without the possibility of turning. Therefore, it is not recommended to use this unit in any way other than for its intended purpose - opened/closed.
Ball valve for shut-off only
Adjustment valves
Designed to balance the entire heating system, and not to adjust the specific radiator on the return line of which they are installed. Quite often, it is necessary to first increase the hydraulic resistance for some radiators so that the coolant is distributed evenly across the heating devices.
For example, in a dead-end circuit with up to 4 radiators, balancing is usually not required and such a valve may not be installed. But with 5 radiators, it is desirable to increase the flow resistance on the first one so that the last one is not cold. And at 6, balancing is already needed on the first three radiators... In reality, the intricacies of pipes from experienced installers can be the most intricate, so they use the settings.
Adjustment on radiators
There are two types of control valves for radiators - manual and automatic, controlled by a thermal head or a servo. They serve as adjustments to quickly configure a specific radiator according to the user’s wishes. “I wanted it cooler - I went up and turned it off...”
Thermal heads control pressure control valves depending on the air temperature - a popular option for equipping batteries. But automation cannot be used in conjunction with solid fuel boilers without a heat accumulator.
Control taps and savings
The control valve is most useful because of the opportunity to save significantly. You can make secondary rooms cold and this gives up to 30% savings on heating in the house per season. If there is programmable automation (electronic thermal heads or a processor with servo drives), then you can set the “day-night” mode in such a way that the house warms up only in the evening, when the occupants are at home, and during the night it cools down and is cold during the day... But this saving, according to the European model, is quite impressive.
What taps to equip a radiator with?
- With extreme savings, they don’t install taps on radiators at all, hoping “at chance.”
- The minimum set is two ball disconnect devices.
- The usual option is a ball on the return and manual adjustment on the feed. You can adjust the device as desired and, if necessary, keep the adjustment as balancing.
- Adjustment - balancing on the return and adjustment on the supply - is used where it is necessary to balance a specific radiator.
- Automatic operation - there is automated adjustment on the supply, while the return may have a ball valve or balancing.
When the pipes are under the floor - bottom connection
Radiators with bottom connections are increasingly being used, and pipes are hidden under the floor. In this case, a radial wiring diagram from one collector is often used. In this case, the shut-off and control valves are installed on it, and a couple of tubes rise to the radiator and that’s it. But if balancing/adjustment is needed, manufacturers offer a connecting kit.
Diagram of the usual connection of radiators with bottom wiring in a radial system
It is also not uncommon for radiators with side connections to be used for underground wiring. Manufacturers also took care and supply heating devices with a set of “adjustment-balancing” valves, between which a jumper is installed to power the supply.
The heating system often includes control mechanisms and mechanisms that ensure safe operation. They are otherwise called heating system valves. With the help of these adjustment elements, the heat supply parameters change; they also ensure stable operation and perform automatic adjustment. Let's look at the valves and regulators of the heating system, since their purposes and functions differ.
Three way heating valve
Typically, boiler automation cannot meet the need for water at different temperatures for several circuits of the heating system. A three-way thermostatic mixing valve of the heating system comes to the rescue, which maintains the necessary thermal parameters of the coolant in the circuits of the heating system, as well as in the small circuit of the system. The valve looks like a simple tee, the metal is bronze or brass. An adjusting washer is installed at the top of this tee, under which there is material sensitive to temperature changes. And if necessary, it presses on the working rod coming out of the housing. The main task of the valve is based on maintaining the temperature of the coolant at the outlet within specified limits by adding cold or hot water . During unsuitable temperature changes, the external valve actuator presses on the stem. Next, the cone leaves the saddle and a passage opens between all channels. During operation, the three-way valve is controlled according to temperature by an external actuator.
Ball valve: how to replace it with your own hands?
Due to the fact that it has a slightly different device, installing taps on radiators, as well as replacing them, can create minor difficulties. Although the repair itself does not take much time: after unscrewing the nut, a new oil seal or valve axle box is installed, and then the nut is returned to its place. However, even before repairing the ball valve, you need to prepare the necessary materials.
Materials
To repair a ball valve, you need to ensure you have the following tools:
- screwdrivers;
- pliers;
- hex wrench;
- gloves;
- used spare parts.
Heating check valve
A complex heating system contains a fairly large number of auxiliary elements, the task of which is to ensure reliability and uninterrupted operation. One of these elements is the heating system check valve. A check valve is installed to prevent flow in the opposite direction . Its elements have very high hydraulic resistance. Due to this circumstance, there are restrictions on the use of check valves in a heating system with natural circulation. There is too little pressure in such a system. At minimum pressure, it is necessary to install gravity valves with a butterfly valve; some of them can operate at a pressure of 0.001 bar. The main part of the check valve is the spring, used in almost all models. It is the spring that closes the shutter when normal parameters change. This is the principle of operation of a check valve.
It is necessary to take into account the operating parameters in a particular heating system. Therefore, select a heating system valve that has the required spring elasticity. Shut-off valves used in heating systems are usually made of the following materials: steel; brass; stainless steel; gray cast iron. Check valves are divided into the following types: disc valves; petal; ball; bivalve. These types of valves are distinguished by a locking device.
What to consider when installing taps
When installing various taps, it is necessary to take into account, firstly, personal preferences, that is, whether you want to overpay for more precise temperature control, and secondly, the parameters of the room, house, and so on.
The instructions for installing shut-off valves of various types are very similar to each other. It is imperative to check everything for leaks in order to avoid accidents; you also need to take into account the convenience of using such devices. You shouldn’t waste money on a seal; it’s better to choose trusted manufacturers.
If you do not understand anything about installing shut-off valves, then it is better to consult with a professional about what type of faucet you should install in your home.
Heating control (shut-off and control) valves
Regulating and shut-off and control heating valves systematically change the flow of coolant, from maximum to minimum , with the valve open and closed. Shut-off or shut-off valves control the coolant discretely when the valve is in the fully open or fully closed position. A control valve consists of three main blocks: the body, the throttle assembly, and the valve actuator. The closing and regulating element of the valve is the throttle assembly. When choosing a sleeve, seat, or plunger, you should pay attention to the operating conditions of the valve. The medium and its temperature, the presence of impurities, and throughput are taken into account. The main and important importance in the operation of the valve is the correct direction of supply of the working medium. It is usually marked with an arrow on the working surface of the case.
Characteristics of thermal valves
For your information, here are a number of basic technical characteristics of thermostatic valves:
- The maximum operating pressure level is 1.0 MPa.
- Pressure testing before commissioning is 1.5 MPa.
- The maximum operating temperature is +110 ºС.
- The maximum permissible ambient temperature is +50 ºС.
- The valve capacity is from 1.6 to 2.5 m³/h.
- Temperature control range - +20…+60 ºС.
- Response time: 25 min.
- MTBF with manual control - 8000 cycles.
What materials are they made from?
Corrosion-resistant metals are used to make the thermostatic valve body:
Additionally, the surfaces of brass products are nickel-plated, and the bronze body is either also nickel-plated or coated with a layer of chrome.
Thermostatic valve
In modern realities, a thermostatic valve is a prerequisite for modern and reliable equipment in a heating system. The valve temperature is automatically adjusted. The operation of a heating system mixing valve for radiators is to limit the supply level to an individual heating radiator. The valve stem makes movements to open and close the hole. Through this hole, coolant enters the radiator. When the valve with a thermostatic head heats up, the inlet opening is closed, as a result of which the coolant flow rate decreases. The thermostatic valve constantly changes its position. And an important factor is the quality of the materials on which this product is made. The product may fail due to sticking of the rod, as well as significant corrosion and breakthrough of sealing materials. But even if the thermostatic valve fails, you can extend its service life by replacing the thermostatic element.
Heating system valves with thermal heads differ depending on the shape and type of supply to the heating system. They can be angular when connected to radiators from the floor, or they can be straight, which connect the pipes to the battery relative to the wall surface. Axial, mainly when connecting pipes from the wall to the battery. When connecting batteries sideways, a special kit is required. It uses thermostatic heads and valves. Batteries that come with a bottom connection are obviously equipped with valve-type inserts.
Selecting a specific radiator model
Once you have decided on the type and type of heating radiators you need, it’s time to calculate and select specific models of these radiators that will have the necessary technical parameters.
Calculating thermal power
How to choose the right heating radiators to achieve the proper level of warmth and comfort? To do this, you need to calculate the thermal power of the radiators you plan to purchase. For certain standard conditions, a thermal power of 0.09 to 0.125 kilowatts per square meter of room is required. This is exactly the power that should be enough to create optimal climatic conditions in the room.
Now about what is meant by standard conditions. Everything is simple, this is a room in which there is a window with a wooden frame and three-meter (no higher) ceilings, as well as an entrance door. At the same time, hot water at a temperature of seventy degrees flows through the heating pipes. If you have the same conditions, then multiplying 0.125 by the area of the room you will get the power of the radiator or radiators (if several are required) required for the room. Next, all that remains is to look at the passport of specific radiators and, having found out there the thermal power of one section or the entire radiator, select the required model.
But this is a simple calculation; in fact, it is necessary to take into account some other factors that will have an impact in this case:
- You can reduce the power of radiators by 10 - 20% if you have plastic energy-saving double-glazed windows installed in your room, because they reduce heat loss in the room by approximately that amount.
- If there are not one, but two windows in the room, then you need to place a radiator under each of them. Their combined capacity should be 70% higher than the standard value. We will do the same in the case of a corner room.
- When the hot water temperature increases or decreases for every 10 degrees, we also increase (or decrease) the power of the device by 15-18%. The thing is that if the temperature of the coolant decreases, then the power of the heating radiators decreases.
- If the ceilings are higher than three meters, the heating power must again be increased. The increase must be made as many times as the 3-meter ceilings in the room are higher. If the ceilings are lower, then you need to make a reduction.
When making calculations, we will take into account how our radiators will be connected. Here are some recommendations on this matter:
- If the coolant enters the radiator from the bottom and comes out from the top, then a fair amount of heat will be lost - from 7 to 10%.
- The lateral one-sided supply makes it unreasonable to install radiators longer than 10 sections. Otherwise, the last sections of the pipe will remain practically cold.
- Gluing a special reflective insulating material to the wall behind the radiator increases heat transfer by 10 to 15 percent. For example, it could be a material such as Penofol.
Determine the required dimensions
When buying a radiator, you need to know exactly the following points:
- What type of eyeliner do you have - hidden or open?
- How are the pipes connected to the radiator, from the floor, from the wall, from above, from the side, etc.;
- Diameter of heating pipes;
- Distance between pipes (center distance).
We also provide for placing the radiator in such a way that air can flow freely around it - otherwise the room will not receive 10 to 15% of heat. The standards for placing radiators are as follows:
- The radiator distance from the floor is from 7 to 10 cm;
- distance from the wall – from 3 to 5 cm;
- distance from the window sill – from 10 to 15 cm.
Basic standards for the placement of radiators.
The final stage of purchasing radiators
Now, if you have autonomous heating, you can, taking these calculations with you, feel free to go to the store to buy heating appliances. But for residents of a high-rise building with a centralized heating system, it makes sense to first go to the emergency room after finding out what the operating pressure is in your heating system. We will build on this parameter when deciding which heating radiator is better to choose. The pressure indicated in the device passport must be higher than that indicated by the DEZ employees in order to obtain a certain reserve. After all, do not forget that in each new season, heating devices are tested with pressure testing, which is 1.5 times greater than the working one.
Pressure regulator
The operation of the batteries and the pump is disrupted due to high or low pressure levels. Correct control of the heating system will help to avoid this negative factor. The pressure in the system plays a significant role, it ensures that water gets into the pipes and radiators. Heat loss will be reduced if the pressure is standard and maintained. This is where water pressure regulators come to the rescue. Their mission is primarily to protect the system from too much pressure . The operating principle of this device is based on the fact that the heating system valve located in the regulator works as a force equalizer. Depending on the type of pressure, regulators are classified into: statistical, dynamic. It is necessary to select a pressure regulator based on throughput. This is the ability to pass the required volume of coolant, in the presence of the required constant pressure drop.
Types of control valves and their parameters
Varieties of special shut-off valves for controlling the heat supply to the radiator include:
- regulators made in the form of valve mechanisms with thermal heads that set a fixed temperature;
- ball valves;
- special balancing valves, manually controlled and installed in private houses - with their help it is possible to evenly heat the interior spaces;
- bleeding air valves - Mayevsky’s manual mechanisms and more advanced automatic air vents.
Ball
With thermal head
Mayevsky crane
The Balancing
List is supplemented with samples of valve regulators used for flushing batteries and draining water. This class also includes a check valve that prevents the movement of coolant in the opposite direction in networks with forced circulation.
Indicators characterizing the operation of any type of shut-off valves include:
- standard sizes of devices, according to which they are selected for specific types of radiators;
- pressure maintained in operating conditions;
- media temperature limit;
- product throughput.
To correctly select a shut-off valve, you will need to take into account all the parameters together.
Heating bypass valve
To relieve the working medium, use the bypass valve of the heating system thermostat, which operates in the return direction when the pressure increases significantly . As a rule, the pressure increases due to the achievement of the maximum temperature set manually, the supply of coolant to the radiator decreases, as a result of which the pressure increases. Heating system bypass valves are basically designed to ensure a stable difference between the return and supply pipes. When the heat load decreases, the thermostatic valves close, resulting in a pressure difference between the pipelines. As a result of using a bypass valve, the load on the pump is reduced, the return temperature increases, and the boiler is protected from corrosion. The scope of application of the heating system bypass valve is quite wide; it is also used to prevent noise generation of thermostats. Bypass valves are installed not only on an unregulated pump, but also on riser jumpers.
Types of devices
Today there are several types of thermostatic valves. Among them the most popular are:
- Mechanical. They require manual adjustment of the coolant supply.
- Semi-electronic. They are controlled by a special thermal head with a bellows device.
- Electronic. Control is carried out using a remote temperature sensor.
Mechanical thermostats
The main advantages of mechanical structures are low price, smooth and precise functioning, and ease of use. During their operation, you do not need to use auxiliary energy sources. Thanks to their modification, it is possible to manually regulate the volume of coolant entering the radiator, controlling its heat transfer. In such devices you can accurately set the degree of heating.
The main disadvantage of mechanical equipment is the lack of markings for adjustment, so its adjustment is carried out mainly by trial and error. The product consists of:
- a bellows filled with a liquid or gaseous mixture;
- regulator;
- drive.
The main role is played by the substance with which the bellows is filled. When the position of the thermostat lever changes, it enters the spool, adjusting the rod. The latter, under such influence, blocks the passage, thereby limiting the entry of coolant into the radiator.
Electronic temperature sensors
Electronic devices are more complex, because they are based on a programmable microprocessor. Thanks to it, it becomes possible to set the required temperature in the room. To do this you need to press several buttons. There are multifunctional models with which you can control a mixer, boiler or pump.
Safety valves
Any boiler equipment is a source of danger. Boilers are considered explosive because they have a water jacket, i.e. pressure vessel. One of the most reliable and widespread safety devices that reduces the danger to a minimum is the safety valve of the heating system. The installation of this device is due to the protection of heating systems from excess pressure . Often this pressure occurs as a result of boiling water in the boiler. The safety valve is installed on the supply pipe, as close to the boiler as possible. The valve has a fairly simple design. The body is made of good quality brass. The main working element of the valve is the spring. The spring, in turn, acts on the membrane, which closes the passage to the outside. The membrane is made of polymer materials, the spring is made of steel. When choosing a safety valve, it should be taken into account that full opening occurs when the pressure in the heating system increases above the value by 10%, and full closure occurs when the pressure drops below the response value by 20%. Due to these characteristics, it is necessary to select a valve with a response pressure higher than 20-30% of the actual one.
Expert advice
A few tips from professionals will help the apartment owner install and configure the thermostatic valve with his own hands and in accordance with all the rules:
- It is important to mount the device in such a way that the direction of water movement coincides with the direction shown by the arrow shown next to the marking on the body, otherwise the operation of the thermostatic valve will be incorrect.
- For underfloor heating systems, it is better to choose thermostats with a side valve - this makes settings easier to access.
- In public areas, thermostatic valves with remote control or pre-setting should be used for installation to protect them from outside influence.
- To seal the threaded connection, you should not use fum tape, but polymer or linen threads with heat-resistant paint. When heated and significant temperature changes occur, thermal expansion of the pipes occurs, the density of the tape may be disrupted, which will lead to the formation of a leak.
- It is more appropriate to place the valve on the supply pipe.
- The distance from the floor to the installation site of the thermostatic valve should be at least 40-60 cm. Initially, manufacturers configure them to capture temperature changes at this level. If it is necessary to change this parameter, then additional configuration of the device is performed.
- The thermostatic head must be installed on the valve in a horizontal position and turned towards the inside of the room. If you install the thermal head vertically, the warm air from the riser will interfere with the normal operation of the sensor.
- When installing a thermostatic valve in a one-pipe heating system, it is necessary to install an additional bypass section - a bypass. It should be located between the sections of pipelines entering the heating device and leaving it (as in the photo below).
Source
Balancing valve
The balancing valve of the heating system is intended to regulate the coolant passing through . Liquid consumption depends on pressure. The higher the pressure, the more fluid is consumed. This device is installed on risers. A balanced system ensures continuous operation. The manual valve is used as a diaphragm, and the automatic valve maintains pressure and consumption in the risers. A manual balancing valve can shut off the system. The design is a valve type device. Manual valves can be installed in conjunction with shut-off valves.
Flow regulator
Having installed energy metering devices, the question naturally arises of how you can regulate and control the supply of coolant, limit or add its flow. For this purpose, there are all kinds of automatic regulators, the use of which allows you to save money; they operate from outside air temperature sensors and return pipeline sensors. Another advantage of temperature controllers is that they control the temperature directly at the radiator installation site, unlike other devices. This advantage gives priority in obtaining a uniform temperature background for a comfortable stay in the room. The regulator will prevent overheating of the air in the room, which sensors on centralized automation cannot always track. It is possible to adjust the temperature for each room separately. Sometimes, when solving the adjustment issue, ordinary taps are installed. Of course, this solution reduces financial costs, but deprives a number of useful advantages. The faucet has limited functionality to open and close. There is a danger of stopping or airing the riser. By adjusting the heating using taps it is impossible to achieve the required temperature. Using automatic regulators, you can adjust the system accurately and efficiently.
Ways to increase the heat transfer of batteries
The presence/absence of the opportunity to increase heat transfer depends on the calculation of the radiator power reserve. If the device is not able to produce more thermal energy, then no fittings will help.
You can try to change the situation in one of the following ways:
- First of all, you should check whether the filters and pipes are clogged. Blockages form both in old buildings and in new buildings, as various construction debris enters the system. When cleaning does not produce results, drastic measures need to be taken.
- Increase in coolant temperature. This can be done if there is an autonomous heating supply, but with centralized heating it is unlikely.
- Changing the connection type. Not all battery connection methods are equally effective. For example, a reverse side connection reduces power by about a quarter. The location of installation of the device also affects the heat transfer.
- Increasing the number of sections. If the location and method of connecting radiators are chosen correctly, and the room is also cold, this means that the thermal power of the devices is not enough. Then it is necessary to increase the number of sections.
If the heating system is equipped with batteries with temperature control, then they require a certain power reserve and this is their main drawback. As a result, heating installation costs increase, since each section costs money.
Comfort cannot be achieved if the room is cold or too hot, so adjusting the heat in radiators is a universal solution to this problem.
There are many devices on sale that are designed to change the volume of coolant passing through the radiator. Among them there are both inexpensive and high-cost products. They come with different adjustments: manual, electronic and automatic.