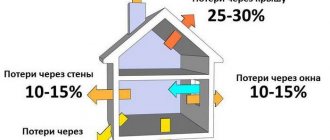
Residents of apartments equipped with a central heating system often notice that from year to year the efficiency of heating the premises becomes less and less. They have to add additional heat sources - electric radiators, which heat efficiently, but locally. In addition, electricity bills significantly increase your overall utility bills.
There is another way out of the situation - using simple ways to increase the heat transfer of a central heating radiator.
There is no need to invite a specialist or purchase additional tools - everything can be done with your own hands, using available tools.
How to regulate radiators
To understand how temperature regulation occurs, let’s remember how a heating radiator works. It is a labyrinth of pipes with different types of fins to increase heat transfer. Hot water enters the radiator inlet, passing through the labyrinth, it heats the metal. This, in turn, heats the air around it. Due to the fact that modern radiators have specially shaped fins that improve air movement (convection), hot air spreads very quickly. During active heating, there is a noticeable flow of heat from the radiators.
This battery is very hot. In this case, the regulator needs to be installed
From all this it follows that by changing the amount of coolant passing through the battery, you can change the temperature in the room (within certain limits). This is what the corresponding fittings do - control valves and thermostats.
Let's say right away that no regulators can increase heat transfer. They only lower it. If the room is hot, install it; if it’s cold, this is not your option.
How effectively the temperature of the batteries changes depends, firstly, on how the system is designed, whether there is a reserve power of the heating devices, and secondly, on how correctly the regulators themselves are selected and installed. The inertia of the system as a whole, and the heating devices themselves, plays a significant role. For example, aluminum heats up and cools down quickly, while cast iron, which has a large mass, changes temperature very slowly. So there is no point in changing anything with cast iron: it takes too long to wait for the result.
Options for connecting and installing control valves. But to be able to repair the radiator without stopping the system, you need to install a ball valve before the regulator (click on the picture to enlarge its size)
Conclusion: how to make your apartment warmer
In fact, it is impossible to actually increase the amount of heat without changing the input parameters of the system (radiator material, its size, heating temperature). Using the above methods, there is a chance to use this heat more efficiently - completely, with maximum efficiency and optimal distribution in the apartment. For example, a screen will prevent thermal energy from being lost, and a fan will allow the warm air flow to spread more evenly.
If the apartment is cold, and this interferes with the normal life of the owners, more radical measures will have to be taken. These include:
- replacing old cast iron batteries with modern bimetallic radiators;
- “increasing” the number of sections on the battery;
- insulation of the wall behind the radiator and installation of a powerful steel screen.
When carrying out a major overhaul of the heating system, you need to remember: even the highest quality appliances need to be updated after 20–25 years, as their service life is coming to an end. It is worth choosing batteries from the most “advanced” materials of modern design - they are the most energy-intensive and will certainly help make the apartment warmer and more comfortable.
Ways to increase heat transfer
From the point of view of releasing the maximum amount of heat into space, it is less effective than a pipe, perhaps a ball. It has an even worse surface to volume ratio.
What did the ancestors do to make these monstrous heating devices warm?
How to increase the heat transfer of a pipe?
Increased infrared radiation from the heating device. Simply painting the register with matte black paint gave a noticeable warming effect in the room. By the way, the current chrome plating of modern bathroom coils looks impressive, but from the point of view of the heat transfer of the device, it is pure idiocy.
The heat transfer of steel pipes can also be increased due to fins welded or otherwise mounted on the outside of the pipe. The final stage of implementation of this method is a convector, a coil of pipe with transverse plates. Of course, in this case, all methods for calculating the heat transfer of a pipe are not applicable - the pipe gives off a smaller portion of the heat in this device.
Install a reflective screen behind the battery
The battery distributes heat in all directions, that is, it also heats the wall facing the street. A reflective screen attached to the wall behind the radiator will help direct all the heat into the room. The most affordable option is made from foil-isolon - a foamed synthetic material (polyethylene) covered with foil on one side. You can use regular baking foil.
From sheet material you need to cut a screen wider and 10-20 cm higher than the radiator, place it behind the battery with the foil side in the room. To secure the screen, any glue, liquid nails or double-sided tape will do.
The foam material will trap air, thereby creating additional thermal insulation, and the foil will reflect heat, directing it into the room.
Determination of heat transfer
To correctly select the size of registers for space heating in accordance with heat loss, it is necessary to know the heat transfer value of a 1 meter long pipe. This value depends on the diameter used and the temperature difference between the coolant and the environment. The temperature difference is determined by the formula:
∆t= 0.5·(t1 + t2) – tк,
where t1 and t2 are the temperatures at the inlet and outlet of the boiler, respectively;
tk – temperature in the heated room.
The heat transfer table for 1 m of steel pipe will help you quickly determine the approximate value of the amount of heat received from the register. Despite the fact that the result is very approximate, this method is the most convenient and does not require complex calculations.
For reference: 1 BTU/hour · ft2 ·oF = 5.678 W/m2K = 4.882 kcal/hour · m2 ·oC.
The table shows what the heat transfer of steel pipes in an air environment will be at certain temperature changes. For intermediate temperature differences, calculations are performed by interpolation.
To more accurately determine the amount of heat produced by a steel pipe, you should use the classic formula:
Q=K ·F · ∆t,
where: Q – heat transfer, W;
K – heat transfer coefficient, W/(m2 0С);
F – surface area, m2;
∆t – temperature difference, 0С.
The principle of determining ∆t was described above, and the value of F is found using a simple geometric formula for the surface of a cylinder: F = π d l,
where π = 3.14, and d and l are the diameter and length of the pipe, respectively, m.
When calculating a section 1 m long, the formula takes the form Q = 3.14·K·d·∆t.
Note: when determining the heat transfer of a single pipe, it is enough to substitute the reference value of the heat transfer coefficient for steel when transferring heat from water to air, which is 11.3 W/(m2 0C). For a heating device, the K value depends not only on the material from which the pipes are made, but also on their diameter and the number of threads, since they influence each other.
The average values of heat transfer coefficients for the most popular types of heating devices are shown in the table.
Important! When substituting values into formulas, you must carefully monitor the units of measurement. All quantities must have dimensions that are consistent with each other
Thus, the heat transfer coefficient found in kcal/(hour m2 0С) must be converted to W/(m2 0С), taking into account that 1 kcal/hour = 1.163 W.
Of course, the heat transfer table for steel pipes allows you to get results faster than calculations using formulas, but if accuracy is important, you will have to tinker a little.
To determine the required register size, the required thermal output must be divided by the heat output of 1 meter, rounded up to the nearest whole number. As a guide, you can take the average data for an insulated room up to 3 m high: 1 m of register with a diameter of 60 mm is capable of heating 1 m2 of room.
Note: As can be seen from the table, the K coefficient for steel pipes can vary from 8 to 12.5 kcal/(hour m2 0C). Increasing the diameters and number of threads leads to a decrease in the efficiency of heat transfer. In this regard, to increase the heat transfer of the register, preference should be given to increasing the length of the elements.
It is also necessary to take into account that large pipes require an increased volume of water in the system, which creates additional load on the boiler. The recommended distance between the threads is equal to the diameter of the pipes plus another 50 mm.
If the system is filled not with water, but with a non-freezing liquid, then this significantly affects the heat transfer of the register and requires an increase in its size after additional calculations. This is especially true when using devices with heating elements and oil as a coolant.
Steel pipeline is a fairly strong, durable product with good heat dissipation. Registers made of smooth pipes can have various configurations, are very easy to maintain and do not require periodic washing. This allows them to successfully compete with lightweight bimetallic and aluminum heating devices, as well as with traditional “indestructible” cast iron radiators.
Water and gas pipes are widely used in external heating networks when laid open due to their high rigidity and wear resistance. The feasibility of using steel pipes for space heating is determined by operating conditions, financial capabilities and aesthetic taste of the owners. The use of registers is most justified in production and technical premises, but in other cases they have their advantages.
Author (Site Expert): Irina Chernetskaya
Placement of heating devices
It is of great importance not only how to connect heating radiators to each other, but also their correct location in relation to building structures. Traditionally, heating devices are installed along the walls of rooms and locally under windows to reduce the penetration of cold air flows in the most vulnerable place.
There are clear instructions for this in SNiP for installing heating equipment:
- The gap between the floor and the bottom of the battery should not be less than 120 mm. When the distance from the device to the floor decreases, the distribution of heat flow will be uneven;
- The distance from the back surface to the wall on which the radiator is mounted should be from 30 to 50 mm, otherwise its heat transfer will be impaired;
- The gap from the top edge of the heating device to the window sill is maintained within 100-120 mm (no less). Otherwise, the movement of thermal masses may be hampered, which will weaken the heating of the room.
Bimetallic heating devices
To understand how to connect bimetallic radiators to each other, you need to know that almost all of them are suitable for any type of connection:
- They have four possible connection points - two upper and two lower;
- Equipped with plugs and a Mayevsky valve, through which you can bleed the air collected in the heating system;
A diagonal connection is considered the most effective for bimetallic batteries, especially if we are talking about a large number of sections in the device. Although it is not advisable to use very wide batteries equipped with ten or more sections.
Advice! It is better to think about the question of how to properly connect two heating radiators of 7-8 sections instead of one device of 14 or 16 sections. It will be much easier to install and more convenient to maintain.
Another question - how to connect sections of a bimetallic radiator may arise when rearranging sections of a heating device in various situations:
The place where you plan to install the heating device is also important.
- In the process of creating new heating networks;
- If it is necessary to replace a failed radiator with a new one - bimetallic;
- In case of underheating, you can expand the battery by connecting additional sections.
Registers
The simplest design is registers. These are medium- or large-diameter pipes welded at the ends, single or connected in sections by jumper tubes. They can be seen in entrances, at industrial facilities or in private houses with individual heating.
To increase their thermal power, they use a method of increasing the area - thin metal plates are welded. This improves the heat transfer of the battery by almost one and a half times. Compact radiators, the closest relatives of cast iron accordion batteries, have approximately the same heat transfer. Although they are, of course, far from panel bimetallic devices.
To ensure maximum heat transfer from heating radiators, a simple and inexpensive convection method is used. This method involves hanging the device correctly. It is installed as close to the floor as possible, where cold air accumulates, but the gaps necessary for circulation are left, including near the wall itself.
With this installation, the battery sections come into contact with a medium that has the lowest possible temperature under the given conditions, that is, the thermal pressure increases. And the air heated by the registers, thanks to the gaps left, rises freely, and the room is heated faster.
An excellent method is to increase the heat transfer surface area. They do this in different ways:
- By increasing the total length of the heating pipes by forming them into U-shaped registers.
- With fins - strictly speaking, this method increases not specifically the thermal conductivity of the steel pipe, but of the entire radiator, but the power increases by 50%.
- Increasing the number of sections.
Black surfaces have the best heat transfer, but not every interior will fit such a dark battery, which is why this method has not found application. Registers traditionally continue to be painted white.
What to do if the batteries do not heat up
Number of sections
The first thing to do is to calculate whether there are enough radiator sections for your room. If there are not enough of them, then there is only one way out - select the necessary heating radiators and add several sections to the battery.
Standard method for calculating the number of heating radiators: 16 sq.m. x 100W / 200W = 8 where 16 is the area of the room, 100W is the standard thermal power per 1 m², 200W is the approximate power of one radiator section (can be viewed from the passport), 8 is the required number of heating radiator sections
Regulator check
If your battery is equipped with a power regulator, then it is worth checking at what temperature it is turned on. In the spring, there is no need to heat the room very much and, perhaps, the regulator is set at an insufficient temperature now.
Airlock
Check the surface temperature of the battery itself; if it is very hot in one place and barely warm in another, then most likely an air lock is preventing good warming up.
Another symptom of an air lock is an incomprehensible noise, gurgling. Modern batteries have a special valve for bleeding air (Mayevsky tap), it is located at the top of the battery and is opened using a flat screwdriver. It is enough just to unscrew the tap a little until you hear air coming out, wait until all the air comes out and water comes out, and then tighten the tap. Don't forget to provide something to catch the water. If you don’t risk it yourself or haven’t found a similar valve on your battery, then call a plumber.
Radiator cleaning
Dust and dirt greatly interfere with the quality of the battery. You can clean it from the outside yourself. It is better to remove the old layer of paint, if there are several layers, then the procedure is mandatory, and paint it with a special heat-resistant paint, preferably a dark (black) color. Only a plumber using special equipment can clean the battery from the inside.
Decorative casing
The decorative screen (casing) will regulate and increase heat transfer. Moreover, at the moment there is a wide choice of screens; they will not easily fit, but will also decorate any interior. But you need to carefully consider the material from which it is made. A screen made of wood or plastic will not give the desired effect and, on the contrary, will not let some of the heat into the room. In order to make the room warmer, the screen must be made of aluminum; it will conduct heat perfectly.
Little tricks to increase the output temperature of heating batteries
The battery needs free access to air, remove everything that blocks it, including curtains, you can simply lift them onto the windowsill. An ordinary fan can help move air. Position it so that the flow goes past the battery. Thus, warm air will get deeper into the room faster, and cold air will get closer to the radiator.
Some of the heat is absorbed by the wall behind the radiator. To avoid this, you need to insulate this area. Corrugated cardboard and aluminum foil can serve as insulation. Attach this structure to the wall with cardboard and to the radiator with foil. The heat reflection will be simply excellent.
It is not necessary to use improvised means; there are better, more convenient solutions for thermal insulation. Modern materials, such as polyrex, penofol or isolon, are excellent insulators, and on one side have a self-adhesive surface, which, naturally, will facilitate their installation.
Note. After gluing the insulation, the distance between the radiator and the wall should not be less than two centimeters, otherwise the air will not circulate and will not become warmer
If the distance is insufficient, you can simply stick foil; it is better to maintain the distance and not take risks by gluing a thick layer of insulation.
The radiators may not heat well if they are installed so that the gap between them and the wall is initially less than two centimeters; in this case, it is worth thinking about reconstructing them, since half of the heat will go into the wall and will not be able to get inside the room.
The use of technical solutions can, in principle, eliminate the need to install new batteries. Thanks to these little tricks, you can simply raise the temperature by a few degrees; if this is not enough for you, then of course you should think about replacing the batteries and external thermal insulation. published econet.ru
Heated towel rails
The bathroom heated towel rail itself is a clear example of how the heat transfer of a pipe can be improved. The “coil” of the device is nothing more than an artificially increased area of thermal radiation. Since previously they were only part of the general heating branch, it was possible to change the diameter. Therefore, the heat transfer area was increased by simply increasing the length.
By the way, a stainless steel water heated towel rail would look good in black. Shiny and chrome-plated products, although they look beautiful, interfere with heat exchange between the pipe and the environment.
For vertically oriented systems, such as radiators, the method of connecting the inlet and outlet pipes matters. The heat transfer of one device with different installations can change significantly:
- 100% efficiency – diagonal connection (hot water inlet at the top, outlet at the back at the bottom);
- 97% – one-sided with top entrance;
- 88% – lower;
- 80% – reverse diagonal (with bottom entry);
- 78% – one-sided with bottom inlet and outlet of waste water.
Heat loss
No less often, the high thermal conductivity coefficient of a steel pipe must be considered as a negative factor. When heat needs to be delivered to the final point to the consumer with minimal losses, the conductivity of steel should be reduced. This need arises on main pipelines and heating mains laid on the surface.
To reduce it to an insulating shell made of mineral wool or expanded polystyrene, use foil thermal insulation that screens the infrared spectrum of radiation. You can also take steel pipes insulated with several layers of foamed polyethylene in production.
To determine the effectiveness of the insulation used, a standard calculation of the steel pipe is made using the heat transfer coefficient. But the result is multiplied by the efficiency of the insulating material. The difference between the two intermediate results will show how effectively the coolant temperature inside the pipe is maintained. If the figure turns out to be unsatisfactory, the thickness of the insulating shell should be increased or a material with lower thermal conductivity should be selected.
WATCH THE VIDEO
In everyday life, the use of decorative screens or hanging appliances, as is the case with a heated towel rail, leads to heat loss and a decrease in the efficiency of steel heating pipes. It is also undesirable to install such equipment in wall niches. The pipes themselves are not to blame for these losses, since they regularly heat the surrounding air and objects, but what this heat is spent on is a question for the owners.
Calculation of the heat transfer of a pipe is required when designing heating, and is needed to understand how much heat will be required to warm up the premises and how long it will take. If installation is not carried out according to standard designs, then such a calculation is necessary.
Heat transfer from heating radiators table - Climate in the house
The main criteria for choosing devices for heating a home is its heat transfer.
This is a coefficient that determines the amount of heat generated by the device.
In other words, the higher the heat transfer, the faster and better the house will be heated.
How much heat is needed for heating?
To accurately calculate the required amount of heat for a room, many factors should be taken into account: the climatic features of the area, the cubic capacity of the building, possible heat loss from the housing (the number of windows and doors, building material, the presence of insulation, etc.). This calculation system is quite labor-intensive and is used in rare cases.
Basically, the calculation of heat is determined on the basis of established approximate coefficients: for a room with ceilings no higher than 3 meters, 1 kW of thermal energy is required per 10 m2. For the northern regions, the figure increases to 1.3 kW.
For example, a room with an area of 80 m2 requires 8 kW of power for optimal heating. For the northern regions, the amount of thermal energy will increase to 10.4 kW
Heat dissipation is a key performance indicator
The heat transfer coefficient of radiators is an indicator of its power. It determines the amount of heat generated over a certain period of time. The power of the convector is influenced by: the physical properties of the device, its type of connection, temperature and speed of the coolant.
The power of the convector, indicated in its data sheet, is determined by the physical properties of the material from which the device is made, and depends on its center distance. To calculate the required number of radiator sections for a room, you will need the area of the home and the heat flow coefficient of the device.
Calculations are made using the formula:
Number of sections = S/ 10 * energy coefficient (K) / heat flow value (Q)
Calculation: 50 / 10 * 1 / 0.18 = 27.7. That is, to heat the room you will need 28 sections. For monolithic devices, instead of Q, we set the heat transfer coefficient of the radiator and as a result we obtain the required number of batteries.
If convectors are installed next to sources that affect heat loss (windows, doors), then the energy coefficient is taken from the calculation - 1.3.
Radiators are used for heating: steel, aluminum, copper, cast iron, bimetallic (steel + aluminum), and they all have different heat flow values due to the properties of the metal.
Comparison of indicators: analysis and table
In addition to the material from which the device is made, the power factor is affected by the center-to-center distance - the height between the axes of the upper and lower outlets. The thermal conductivity also has a significant impact on the efficiency.
Material of manufacture
Copper and aluminum convectors have the greatest heat transfer. The lowest power factor is observed in cast iron batteries, but this is compensated by their ability to retain heat for a long time.
The efficiency of the heater is affected by the correct installation of heating devices:
- The optimal distance between the floor and the battery is 70-120 mm, between the window sill - at least 80 mm.
- The installation of an air outlet (Maevsky tap) is required.
- Horizontal position of the heat device.
Radiators with better heat transfer:
Choosing the right boiler
The further microclimate in the rooms will depend on the gas boiler in the house. Often, such systems are chosen based on the cost benefits (outcomes) of one of the energy carriers. This approach, surprisingly, is the most correct one. When choosing a coolant, you should be guided by the following factors:
Boiler and heated floor
- The degree of complexity of the necessary installation work, which is aimed at installing complex equipment.
- Further degree of ease of use. The cost of its subsequent maintenance plays an important role.
- It is also worth considering the possibility of power outages and its complete shutdown in a particular region.
- Maximum and minimum system power.
- What is the most profitable energy source from an economic point of view?
The fact is that there is no company that produces heating boilers designed for heated floors. You can find models whose instructions contain information regarding its operation with heated water floor systems, but nothing more. The main distinguishing feature of floor circuits from radiator systems is the temperature of the main coolant. When using radiator systems, the coolant temperature can reach 80°C. The water floor pipes are only 55°C.
Boiler characteristics specification
In order to achieve an optimal indoor microclimate, the system must heat up to 40°C. The cooled coolant will have a temperature of 30°C. If radiators and heated floors are used for heating, which are supplied with heated coolant from the same boiler, then choosing a heat generator should not cause difficulties. Not every heat source can work to maintain the optimal temperature. To do this, you can additionally tie the unit.
Difficulties in connections may depend on the choice of one of the types of boiler and heated floor used:
- coal and automatic pellet;
- floor or wall gas;
- solid fuel;
- electric.
Warm floor
Not so long ago, a heated towel rail or room radiator became a continuation of the overall heating system in the apartment, significantly increasing the heating surface area. But water as a coolant in this situation can create many problems.
No matter how reliable steel pipes are, they do not last forever, and joints, especially threaded ones, can leak over time. Just imagine that this happened inside a concrete screed that cannot be easily removed. For this reason, water-based heated floors are practically not used.
If you do decide to implement this system, you will have to think about how to make it as efficient as possible. Power must be calculated with extreme precision. But if the numbers show that heat transfer is insufficient, you need to first take care of increasing the efficiency of steel pipes.
Since this design does not come into contact with the air in the room, but heats the floor materials, you can only play by increasing the length of the pipes. That’s why they are laid in a compact but long “snake”. Thanks to its large surface area, it transfers a lot of heat.
A caveat: when several linear meters of pipe are tightly laid, the heat transfer of the heated floor as a whole will increase, and for each individual segment, not critically, but will decrease.
The reason is that pipes located too close partially exchange heat with each other. A heated zone is created around each, which leads to a slight decrease in thermal pressure.
How to install any radiators
The coolant in central heating has special impurities that negatively affect many radiator models. That's why they are not installed in apartments. In fact, to solve this problem, we need to make sure that instead of the thermal power plant coolant, we use our ordinary water.
For these purposes, you need to install a heat exchanger at the entrance of the central heating risers into the apartment.
A heat exchanger is a device that removes heat from one source and transfers it to another source. Simply put, this is our intermediary who will simply take heat from the thermal power plant and transfer it to our own heating system inside the apartment.
What are the benefits of a heat exchanger?
- Performs the function of a boiler by removing heat
- Allows you to create your own heating system inside the apartment with your own coolant and pressure.
- Allows you to implement any heating options
Using a heat exchanger also has its disadvantages:
- It gets clogged from time to time. Requires dismantling and washing
- In addition to the heat exchanger, it is necessary to install an expansion tank, pump and related fittings.
Having installed the heat exchanger, you can mount any radiator system: radiator, two-pipe and others. You can hide the pipes in a screed. You can use any pipe materials without worrying that they will become unusable. Any brand of radiator can be used.
Heat loss through pipes
In a city apartment, everything is simple: the risers, the supply lines to the heating devices, and the devices themselves are located in a heated room. What's the point of worrying about how much heat the riser dissipates if it serves the same purpose - heating?
However, already in the entrances of apartment buildings, in basements and in some warehouses, the situation is radically different. You need to heat one room and supply coolant to it through another. Hence the attempts to minimize the heat transfer of the pipes through which hot water enters the batteries.
Thermal insulation
The most obvious way to reduce the heat transfer of a steel pipe is to insulate the pipe. Twenty years ago there were two ways to do this: recommended by regulatory documentation (insulation with glass wool wrapped with non-flammable fabric; even earlier, external insulation was generally made solid using gypsum or cement mortar) and realistic: pipes were simply wrapped in rags.
Now there are a lot of quite adequate ways to limit heat loss: here are foam linings on pipes, and split shells made of foamed polyethylene, and mineral wool.
These materials are actively used in the construction of new houses; However, in the housing and communal services system, the limited budget, politely speaking, leads to the fact that pipes in basements are still simply wrapped with piss... um, torn rags.
Changing the radiator connection method
Are you familiar with the situation when half the battery is hot and half is cold? Most often, the connection method is to blame in this case. Take a look at how the device works with a one-way radiator connection with coolant supply from above.
Notice how much worse the distant sections perform
Now let's take a look at the one-way connection diagram with coolant supply from below.
We see the same effect
But here is a two-way connection with supply from above and below.
We see the same effectWe see the same effect
If you find yourself with one of the schemes presented above, then you are out of luck. The most rational from the point of view of operational efficiency is a diagonal connection with a feed from above.
The entire heat exchange area of the radiator is heated evenly, the radiator operates at full power
And what to do in the case when you don’t want to change the pipe layout or it’s impossible? In this case, we can advise purchasing radiators that have some cleverness in their design. This is a special partition between the first and second sections, changing the direction of movement of the coolant.
A special plug turns the bottom two-way connection into the diagonal connection we need with the top connection. And this option is suitable for the top two-way connection
In the case of a one-way connection, special flow extenders have shown their effectiveness.
Operating principle of the flow extender
There are devices for optimizing one-way bottom connections, but we think the general principle has now become clear to you.
Commentary Sergei Kharitonov Leading engineer for heating, ventilation and air conditioning LLC GC Spetsstroy Ask a question “The connection method is one of the most effective ways to increase the heat transfer of the battery or, more precisely, to make the radiator work the way it should. For obvious reasons, it is best to provide for such things at the design stage of the heating system, so as not to rack your brains later. After all, any alteration will require disconnecting the riser, the skills of a mechanic or financial costs, and in some cases, coordination with the housing office.”
Conclusion: 100% effective.
Electric heater elements
Unlike a water system, the screed is heated in this case by applying electric current to the heating element inside the screed. Therefore, the structure of such a system is somewhat different:
- Harness with heating cable inside. It can be single or double-core, depending on the task being solved and the heating rate.
- A thermostat that supplies voltage to the electrode and regulates its operating time. Using a thermostat, you can completely turn off heated floors when they are not needed, for example, in the summer.
- Temperature sensor. This device is placed inside the screed and connected to a temperature and voltage regulator. When reading information, it transmits it to the control panel, so without it being in good condition, the electric heated floor will not work.
For electric film floors, the equipment list will include infrared mats instead of cables.
Summarize. Warm floors are an excellent addition to radiator heating in an apartment, and in some cases, an opportunity to completely do without radiators in your cottage.
Remember that when making calculations and choosing heating, it is a good idea to consult with professionals, for example, equipment suppliers. The installation of elements of water and electrical systems has its own characteristics, but in general, everyone can lay out a homemade “pie” of a heated floor.
Types of heating systems and the principle of adjusting radiators
Handle with valve
In order to correctly adjust the temperature of radiators, you need to know the general structure of the heating system and the layout of the coolant pipes.
In the case of individual heating, adjustment is easier when:
- The system is powered by a powerful boiler.
- Each battery is equipped with a three-way valve.
- Forced pumping of coolant has been installed.
At the stage of installation of individual heating, it is necessary to take into account the minimum number of bends in the system. This is necessary in order to reduce heat loss and not reduce the pressure of the coolant supplied to the radiators.
For uniform heating and rational use of heat, a valve is mounted on each battery. With it, you can reduce the water supply or disconnect it from the general heating system in an unused room.
- In the central heating system of multi-storey buildings, equipped with a vertical supply of coolant through a pipeline from top to bottom, it is impossible to adjust the radiators. In this situation, the upper floors open the windows due to the heat, and the rooms on the lower floors are cold, since the radiators there are barely warm.
- A more advanced one-pipe network. Here, the coolant is supplied to each battery and then returned to the central riser. Therefore, there is no noticeable temperature difference in the apartments on the upper and lower floors of these buildings. In this case, the supply pipe of each radiator is equipped with a control valve.
- A two-pipe system, where two risers are mounted, ensures the supply of coolant to the heating radiator and back. To increase or decrease the coolant flow, each battery is equipped with a separate valve with a manual or automatic thermostat.
Which battery connection diagram is the most efficient?
There are three ways to install a radiator.
Diagonal
It is considered the most effective and is used in most cases.
Photo 1. Four options for diagonally connecting a radiator to heating, for one-pipe and two-pipe systems.
This is due to high efficiency:
- The coolant enters the battery from the top corner.
- The liquid disperses throughout the available volume.
- It flows out at the opposite point.
According to this scheme, systems are tested in factories.
Lower
It is less common than others because it has a lower efficiency. Both pipes are connected to the bottom of the battery. The average loss is 15%.
Photo 2. One-pipe and two-pipe method of lower connection of the heating battery. In the second case, more materials are needed.
One of the advantages is the possibility of installation in the floor, which hides the harness. And to compensate for low efficiency, it is recommended to install a more powerful radiator.
You should not use a similar scheme in a piping without a pump, since a vortex phenomenon occurs. The flow heats the surface of the pipes, increasing heat transfer during natural circulation of water. The phenomenon has not yet been studied, so the possible consequences are unclear.
Lateral or one-sided
True to the name, the pipes are included from one side: at the upper and lower corners. A similar installation option is used in buildings with vertical highways, for example, in apartment buildings. This scheme is not used when supplying coolant from below, since installation is significantly more complicated.
Photo 3. Both one-pipe and two-pipe systems allow for side connection of the battery. In the first case, a bypass is required.
It has high efficiency, slightly less than the diagonal circuit. This applies to radiators with 10 or fewer sections. Long batteries warm up worse, since the working fluid has to travel a long way in one direction.
Important! This factor does not affect panel heat exchangers, in which special rods are installed that improve the flow.
We make a calculation
The formula by which heat transfer is calculated is as follows:
Q = K*F*dT, where
- K – thermal conductivity coefficient of steel;
- Q – heat transfer coefficient, W;
- F is the area of the pipe section for which the calculation is being made, m 2 dT is the value of the temperature pressure (the sum of the primary and final temperatures taking into account room temperature), ° C.
The thermal conductivity coefficient K is selected taking into account the area of the product. Its size also depends on the number of threads laid in the premises. On average, the coefficient is in the range of 8-12.5.
dT is also called temperature difference. To calculate the parameter, you need to add the temperature that was at the outlet of the boiler with the temperature that was recorded at the entrance to the boiler. The resulting value is multiplied by 0.5 (or divided by 2). The room temperature is subtracted from this value.
dT = (0.5*(T 1 + T 2)) - T to
If the steel pipe is insulated, then the resulting value is multiplied by the efficiency of the insulating material. It reflects the percentage of heat that was given off during the passage of the coolant.
Develop good habits
A healthy lifestyle is one of the powerful resources for increasing personal effectiveness. In this case we are talking about several aspects of life
- Switch to a healthy lifestyle: proper nutrition and regular exercise charge you with tremendous energy, increase endurance and make you stronger.
- Master time management: competent planning can increase the efficiency of your work several times.
- Come up with personal rituals that will set you up for a particular activity. For example, freshly brewed coffee and certain music can set you up for intellectual work.
Increased heat transfer.
To effectively increase the radiated heat rate, there are many ways:
- installation of a convector;
- painting pipes with black paint;
- register setting;
- additional battery sections.
The convector is a curved pipe with metal plates. You can make it yourself or buy a more modern analogue in the store.
The use of matte black paint to paint the surface of the coolant also gives a good result. Aesthetically, it doesn’t look very attractive, but when it comes to comfort, you have to choose.
Another inexpensive and fairly popular design is a register. These are several wide pipes connected to each other with welded sections. These also include heated towel rails, radiators, main lines and even an ordinary steel pipe fixed around the entire perimeter of the room.
Increased air circulation
The cause of cold in the apartment may be a lack of air convection. According to the laws of physics, heated air tends upward, and when a wide window sill or a heavy curtain hangs over the radiator, all the efforts of the stokers disappear out of the window.
To avoid an offensive effect, it is better to keep thick curtains open or replace them with transparent tulle, and equip the protruding part of the window sill with slits or decorative openwork inserts.
An effective way to increase the flow of cool air to the battery and the outflow of warm air from it is to install a small household fan on the side, or preferably below. Craftsmen have gotten the hang of connecting several computer coolers together and placing them under the radiator to achieve the best result.
The listed techniques are quite effective, but it is always better to eliminate the cause of the problem rather than deal with its consequences.
Step-by-step instructions for adjusting temperature
To ensure comfortable living conditions in the room, you need to perform some basic steps.
- Initially, it is necessary to bleed the air on each battery until water flows from the tap in a trickle.
- Then you need to adjust the pressure in the batteries.
- To do this, in the first battery from the boiler you need to open the valve by two turns, on the second - by three, and then according to the same scheme, increasing the number of turns of the valve being opened on each radiator. Thus, the coolant pressure will be evenly distributed over all radiators. This will ensure its normal passage through the pipes and better heating of the batteries.
- In a forced heating system, control valves will help to pump the coolant and control rational heat consumption.
- In a flow-through system, the temperature is well regulated by thermostats built into each battery.
- In a two-pipe heating system, you can control not only the temperature of the coolant, but also its quantity in the batteries using both manual and automatic control systems.
Simple ways to increase battery efficiency
To increase the heat transfer of radiators, it is recommended to improve air circulation in the heated room.
To do this, you need to empty the heating batteries as much as possible, that is, remove nearby furniture, remove protective screens and curtains.
This will increase air circulation, which in turn will increase the temperature inside the room.
If the above method does not bring the desired results, then you can speed up the air circulation using fans.
In this case, it should be said that the faster the air moves, the more heat it takes from the radiator and distributes throughout the room.
It turns out that to increase the heat transfer of the radiators, it is necessary to install a fan opposite them. This method is effective, but noisy.
To make such a system quieter and give it greater autonomy, it is recommended to install computer fans. In this case, fans must be installed directly under the batteries.
Using this method, it is possible to increase the temperature in the room from 5 to 10 degrees. It is also worth noting that using computer fans to increase heat transfer from radiators is considered a fairly cheap way.
Another simple way to increase the heat transfer of batteries is to install a heat-reflecting screen behind the radiator. This screen allows you to direct thermal energy directly into the room.
In this case, the ideal option is foil isolon, which is a foam base with foil. It is worth saying that the use of foil isolon will not only direct heat in the right direction, but will also insulate the wall.
To install a heat-reflecting screen, you can use almost any adhesive. It is worth knowing that the screen area should be slightly larger than the size of the radiator.
Summarize
There are many ways to increase the heat output of heating radiators. Today we looked at only the main ones. However, it should be remembered that it is always easier to think through everything in advance, at the installation stage, than to put in a lot of effort later, without the confidence that the result will be significant. Unfortunately, in Russia everything is done at random. The final advice from the Homius.ru editors would be this: think about the future and spare no expense during installation. The financial resources saved today can turn into costs tomorrow that will be many times greater than your savings.
The most optimal option is that all the heat rises, which creates normal heat exchange
We hope that the information presented in today’s article was interesting and useful to our dear reader. Despite the fact that we tried to present everything in sufficient detail, you may still have questions about the material. In this case, ask them in the discussions below - the Homius.ru editors will be happy to answer them as quickly as possible. If you know a way to improve the heat transfer of radiators that is not reflected in today’s article, please share it with other home craftsmen - this information will be very useful. And finally, we suggest watching a short but quite informative video on today’s topic.
Results and conclusions.
- I managed to increase the air temperature in the room by as much as 6ºC, and in extreme fan operation mode even by 9ºC, which confirmed the assumption that it is possible to increase the heat transfer of a central heating battery, even at such a low coolant temperature.
- When using a regular household fan without a speed controller, the room becomes too noisy. However, if you use the heat accumulated in the room, then, for example, you can turn off the fan in the bedroom at night, and, on the contrary, turn it on in the dining room. Then you can use the fan at full power.
- If you are in that part of the room where the movement of air generated by the fan is most noticeable, then a false sensation of a decrease in temperature is created.
- Those who are afraid that the fan will wind up a lot can calculate the monthly energy consumption.
35(Watt) * 24(hours) * 30(days) ≈ 25(kW*hour)
Prologue.
This year we are experiencing unprecedented frosts. In some areas of the republic, the air temperature dropped to -24ºС, which is an anomalous phenomenon for warm Moldova. I don’t have a thermometer hanging in my room, but I felt that my hand lying on the table began to freeze, and I had to put a piece of foam rubber under it.
We, in general, like the Amundsens, are already accustomed to the coolness, but yesterday the chairman of our condominium, while collecting signatures for an appeal to the heat supplier, asked what the air temperature was in our apartment. It is unlikely that the heat supplier will increase the temperature of the coolant, but perhaps the chairman wants to demand a penalty under the pretext of providing poor-quality services.
Be that as it may, this event first prompted me to measure the air temperature in the apartment, and then to conduct this experiment.
Of course, to say that this experiment was unclean is to say nothing. There are too many variables that could affect the accuracy of the result, from the direction of the wind overboard to the activity of the computer running in the room being tested.
But the most important parameter, which at another time would not have allowed this experiment to be carried out at all, is the stability of the coolant temperature.
The fact is that in warmer periods of time, the temperature of the coolant is actively regulated during the day to save energy consumption. When the temperature outside is abnormal, all the valves open wide.