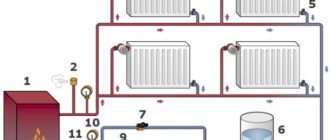
When solving home heating problems, it is necessary to take into account the total number of square meters. When the calculation of area is carried out not in units, but in hundreds, and the building has more than one floor, the system with natural circulation does not cope with its tasks. In such systems, the pressure in most cases is not higher than 0.6 MPa, for this reason a pump cannot be dispensed with. From the article below you can find out what a heating circulation pump is, what types of circulation pumps there are for heating systems, the technical characteristics of these devices, the principle of operation, and also how to choose them correctly.
Principle of operation
Structurally, this pumping equipment resembles a drainage unit: the body is made of stainless metals, equipped with a rotor and a shaft equipped with a blade wheel.
Let's consider circulation pumps for heating systems. The operating principle is based on the following:
The electric motor is driven by a rotor. Such a system takes water on one side and pumps it into the pipeline on the other.
By means of centrifugal force, the coolant moves through the heating system.
The pump helps overcome the resistance that invariably arises in individual sections of the pipeline.
Design features
The pump is designed simply: 2 parallel disks are connected to each other by curved blades and form an impeller. One of them has a hole for coolant flow, and the other has clamps to fix the structure on the impeller motor shaft.
Before using a pump, it is better to first become familiar with its design.
Design elements:
- The body is made of various materials - it can be stainless steel or non-ferrous alloys;
- Rotor;
- Rotor shaft;
- Rotating rotor;
- Impellers or impeller;
- Electric motor.
To direct the liquid in the desired direction and create kinetic energy and pressure, there is a hole in the shape of a spiral (in section). In a fixed wheel, the coolant lubricates and cools the rotor shaft. The stator of the electric motor is placed under voltage, so it is divided by a glass, which is equipped with stainless steel or carbon material. The rotor of the unit is mounted on ceramic bearings. Such pumps are used for heating when recirculating coolant with a constant or slightly variable flow rate.
Varieties
So, there are two main types of pumps: with a “wet” rotor and a “dry” rotor. What does this mean? Let's take a closer look at these circulation pumps for heating systems; we also won't ignore the technical characteristics of these devices.
"Dry"
In this case, the rotor is in no way in contact with the coolant - its working part is separated from the engine by means of o-rings. The efficiency of pumping equipment of this design reaches about 80%. However, the operation of a “dry” rotor is accompanied by a noise effect.
"Wet"
Circulation pumps for heating systems (we’ll look at how to choose this equipment below) with a “wet” rotor, on the contrary, together with the impeller, are immersed in the coolant, which cools the electric motor, while playing the role of a lubricant. In this regard, the noise level created by the engine is significantly lower.
This engine option does not require special maintenance over a long period of time. However, compared to the previous option, its operation is not so effective - the efficiency decreases to 50%. Quietly operating “wet” type equipment is traditionally used in domestic heating systems to circulate coolant.
When choosing pumping equipment for a heating system, it is recommended to take certain parameters into account. Let's look at them in more detail.
Operating principle
Circulation pumps are used to constantly move liquid in a hot water system. To connect them, it is necessary to install a storage tank. Liquid is drawn through the inlet pipe of the pump, which creates a vacuum and water from the storage tank enters the circuit.
The pump impeller pumps the liquid, building up pressure in the outlet pipe, while at the same time the cooled water flows back into the container. Thus, with constant operation of the pump, there is a continuous circulation of coolant in the system.
The principle of operation of the pump in the diagram
The hot water supply circuit does not end at the extreme point of water intake, but is connected to a storage tank. Thus, the liquid constantly circulates in the system, regardless of whether the water intake points are open or closed. For ease of use, a shut-off device can be installed on the return flow pipeline. This will shut off the circuit and stop recirculating the hot water supply if necessary.
System lift level
This is an indicator of the maximum possible pressure that the heating system is capable of. The level of lift in the system reflects the total indicator of hydraulic resistance in the system as a whole.
When calculating the hydraulic resistance, the number of storeys of a heated structure with a closed heating system does not have a decisive value; on average, it is approximately 2-4 m of water. pillar For heating systems traditionally installed in low-rise buildings, this parameter is identical.
The connection diameter and maximum pressure are indicated in the marking of the pumping equipment. For example, consider circulation pumps for Grundfos heating systems. The characteristics of the Grundfos UPS 25-60 pump are as follows: the diameter of the connected pipeline must be 25 mm, and its pressure must be 6 m of water. pillar
There is also pumping equipment from this company with lifting heights of 3, 4 and 8 meters. In this case, their markings indicate the numbers 30, 40 and 80, respectively.
We will also consider circulation pumps for Wilo heating systems (selection instructions are similar to the previous option). For example, the Wilo Star-RS 30/6 pump can be connected to a 30 mm pipeline, and its pressure is 6 m of water. pillar
Pump marking
All the data the user needs is contained in the markings on the front panel. The numbers on the circulation pump mean:
- type of device (most often it is UP - circulation);
- speed control type (not specified - single-speed, S - step switching, E - smooth frequency control);
- diameter of the pipes (indicated in millimeters, means the internal dimension of the pipe);
- pressure in decimeters or meters (may differ among different manufacturers);
- installation dimensions.
The pump marking also contains information about the types of connections of the inlet and outlet pipes. The complete coding scheme and word order looks like this:
Responsible manufacturers always follow standard labeling rules. However, individual companies may not indicate some of the data, for example, installation dimensions. You need to find it out directly from the documentation for the device.
It is worth choosing a pump only from trusted brands. Reliable devices are also available in the mid-price category. And if you need the highest quality and have the opportunity to pay one and a half to two times more, you should pay attention to products from the GRUNDOFS and WILO brands.
Energy requirement
In addition, there is another parameter that needs to be taken into account, albeit indirectly. This is the building's need for heat. The value of this parameter is indicated in the building’s passport during the design process. If this data is not available, then it is easy to calculate it yourself.
Each country has its own heat standards per 1 m2. According to European standards, heating 1 m2 of a one- or two-apartment house will require 100 W and 70 W for an apartment building. Russian standards are established for each specific region in accordance with the requirements of SNiP.
Electricity consumption
Any pumping equipment has up to three connection positions to the electrical network. There is a plate on the body of the device that contains information about the electrical current it consumes. Each switch position will correspond to the new equipment performance, namely the amount of coolant per hour pumped through the heating system by the pump. The third position corresponds to the maximum possible pump performance. The maximum consumption is indicated on the device body.
Serially produced circulation pumps for heating systems have average technical characteristics. It is therefore important to consider the individuality of your heating system.
Why the increased noise in pipelines resulting from excessive pump power (users note this in reviews) when the system is actively operating?
Reviews from experts
The modern market offers a lot of different heating pumps. Among foreign manufacturers, experts highlight Grundfos and Lowara circulation pumps. Also, high-quality high-tech products are supplied by Italian manufacturers of circulation pumps Ebara and Speroni.
Circulation pumps for heating systems "Sprut" with relatively low power are characterized by high efficiency. If you plan to increase the service life of the boiler, save energy, and also ensure optimal thermal conditions in the premises, then this equipment will suit you perfectly.
Evgeniy Filimonov
Ask a Question
Currently, there are many modifications and types of pumping equipment. In most cases, a model range is presented with different flow areas, performance and pressure. As a result, the consumer can choose the best option for his heating system.
The operating principle of the pumps is organized in such a way that the required fluid pressure is ensured through special rotors. As mentioned above, rotary pumps are divided into “wet” and “dry”. The only difference is in the operating conditions of the equipment and its ability to interact with the coolant. If you decide to purchase “dry” or submersible equipment, then circulation pumps for Wilo heating systems are an ideal option - consumer reviews about them are mostly positive. The Wilo brand has long established itself as a manufacturer of durable and high-quality products.
Technical specifications
Pumps supply coolant by rotating blades located inside its body.
When considering circulation pumps for heating systems and technical characteristics, the following must be taken into account:
- productivity - the amount of liquid passed per hour of its operation. It is measured in cubic meters per hour and is determined by the hydraulic resistance of the pipeline;
- pressure – the parameter indicates the maximum height to which the pump raises a column of water;
- Maximum temperature. Since the device will pump heated water in the system, it must withstand temperatures up to 110 degrees Celsius. When choosing, you need to make sure that the equipment is designed for it;
- Pumps with nozzle diameters of 25 or 32 mm are often used.
Usually the calculation is made using the first two parameters.
Choosing a place
When installing such a unit, it is necessary to choose a method for inserting it, taking into account the fact that in the future the device will need to be serviced. In addition to this requirement, there are other points that affect the choice of installation location.
Previously, it was cut into the return line so that the working area was washed with already cooled water, and thereby extended the life of the device. Nowadays, manufacturers produce pumps with parts and assemblies made of materials that are not afraid of exposure to hot water. Therefore, they can be installed not only in the return pipeline, but also in the supply pipeline.
You need to decide where exactly you will embed the device.
To increase the pressure of the coolant, it should be installed on the section of the water supply pipe, placing it closer to the entrance to the expansion tank system. This will ensure high temperatures are maintained.
Before installing it on a bypass (jumper, section of pipe between the direct and return coolant supply), you need to check whether the device can withstand strong pressure of hot water.
If there is a membrane tank, the bypass pump is cut into the return pipeline, preferably closer to the expansion tank. When access to the device is difficult, it can be installed on the supply pipeline, and a check valve can also be installed there.
Room heat requirement
Before choosing a circulation pump for heating, you need to calculate the heat demand of the heated room. Professional designers produce it using special formulas. When it is not possible to access them, you can select the required value approximately, taking into account the size of your room.
According to building rules and regulations, in the Moscow region, for one- and two-story houses, sufficient power is 173 kW/sq.m, and for three to four floors – 98 kW/sq.m. The total heat consumption is found by simply multiplying this value by the area of the entire room.
Equipment performance
To calculate it, use a simple formula: G = Q / (1.16 x ΔT), where Q is the previously found heat demand; ΔT is the difference between two temperatures: supply and return. For a conventional two-pipe system this is 20 degrees C, and for a heated floor - 5 degrees C.
For a house with an area of 100 sq.m. the calculation will be as follows:
Q = 173 x 100 = 17300 kW.
G = 17300 / 1.16 x 20 = 745.689 = 746 cubic meters per hour.
Evgeniy Filimonov
Ask a Question
Calculation of a circulation pump for a heating system includes calculating the pressure required to overcome the resistance of the line. You can find its value in various ways, depending on whether a new system is being installed or the pump will be built into an existing one.
For a new one, this value is calculated using certain formulas using the values specified for fittings, pipes, etc.
For an already installed system, the exact value of this parameter is difficult to find; it is calculated approximately:
- the passage of 1 m of heating pipeline requires 0.01-0.015 m of pressure;
- heat loss in fittings is approximately 30% of the previous parameter;
- the non-return valve, as well as the three-way valve, prevent the normal circulation of the coolant, therefore they are estimated at 20%;
- thermostatic valves installed to regulate room temperature.
The value is calculated as follows: H = R x L x ZF, where:
R is the resistance of straight sections (it is better to take into account the maximum value of 0.015 m);
L is the length of the pipes forming the heating system (two-pipe - the return line is also taken into account);
ZF is a coefficient: if conventional ball valves and fittings are installed, it will be 1.3 (indicated 30% losses), and if a thermostatic valve or throttle that breaks the circuit is 1.7.
Power connection
The circulation pumps operate from a 220 V network. The connection is standard; a separate power supply line with a circuit breaker is desirable. The connection requires three wires - phase, neutral and ground.
Circulation pump electrical connection diagram
The connection to the network itself can be organized using a three-pin socket and plug. This connection method is used if the pump comes with a connected power wire. It can also be connected via a terminal block or directly with a cable to the terminals.
The terminals are located under a plastic cover. We remove it by unscrewing several bolts and find three connectors. They are usually labeled (the pictograms are N - neutral wire, L - phase, and “ground” has an international designation), so it’s hard to make a mistake.
Where to connect the power cable
Since the entire system depends on the performance of the circulation pump, it makes sense to make a backup power supply - install a stabilizer with connected batteries. With such a power supply system, everything will work for several days, since the pump itself and the boiler automation “pulls” electricity to a maximum of 250-300 W. But when organizing, you need to calculate everything and select the battery capacity. The disadvantage of such a system is the need to ensure that the batteries do not discharge.
How to connect a circulator to electricity through a stabilizer
Hello. My situation, a 25 x 60 pump is located immediately after a 6 kW electric boiler, then the line from a 40 mm pipe goes to the bathhouse (there are three steel radiators) and returns to the boiler; after the pump, a branch goes up, then 4 m, down, rings a house of 50 sq. m. m. through the kitchen, then through the bedroom, where it doubles, then the hall, where it triples and flows into the boiler return; in the bathhouse there is a branch 40 mm up, it leaves the bathhouse and enters the 2nd floor of a house of 40 sq. m. m. (there are two cast-iron radiators) and returns to the bathhouse in the return line; there was no heat on the second floor; the idea of installing a second pump in the bathhouse for supply after the branch; the total length of the pipeline is 125 m. How correct is the solution?
The idea is correct - the route is too long for one pump.
Necessary calculations
For example, it is necessary to calculate a circulation pump for heating a square house with an area of 100 square meters - for a single-pipe heating system.
Chokes or thermostats are installed directly on heating devices, and rupture of the main ring is excluded. The length of each wall is 10 m. The total length of the pipes in the circuit will be 10 x 4 = 40 m. Substituting the values into the above formula, you can find the required pressure: 0.015 x 40 x 1.3 = 0.78. It is also necessary to take into account that the selected pump must have a headroom of at least 10%.
Control method
Maintaining the circulation of hot liquid at all times is acceptable, although this is not always economically justified. Many will agree that there is not always a need for such water, so there is no need for the pump to work non-stop. If the pipes are routed correctly and thermal insulation is installed, the liquid will not immediately cool down. As far as monetary costs are concerned, this will not affect them since recirculation pumps are inexpensive to maintain.
The control method can be by timer, that is, schedule, and by temperature sensors.
Nuances of choice
Evgeniy Filimonov
Ask a Question
Having calculated the required values (the combination of these parameters is called the operating point), the desired model is selected. In principle, any of them is suitable, the technical characteristics of which are no worse than those calculated.
However, before choosing circulation pumps for heating systems, you need to take into account the following nuances:
- Typically, when calculating productivity, the highest loads that can occur at the coldest temperatures of the season are taken into account. However, the heating system rarely operates in this mode - only a few days throughout the year. Therefore, if it seems that the pump power is more than necessary, it is better to choose a model whose parameter in question is slightly smaller;
- try to find the position of the calculated operating point on the flow-pressure characteristic curve for each of the proposed pumps. Choose a device where the operating point is located closest to the graph;
- you should carefully select such equipment, because a model with insufficient power will not be able to provide the required pressure, as a result, the radiators will not heat up to the required temperature;
- however, excess power is also not needed, since electricity consumption will increase, and the noise level may also increase;
- It is undesirable for the diameter of the pump nozzles to be smaller than the diameter of the pipes - otherwise it will not be able to maintain the required pressure.
By calculating the power, you can choose the model that is most optimal for economically heating your home.
What to do if the device hums but does not turn?
This problem is faced by those pump owners who do not often use the devices and ignore the need to maintain the heating system. To fix the problem you will need:
- Turn off the power to the unit;
- Drain the coolant from the pump and adjacent pipes;
- Remove the screws that secure the motor housing;
- Remove the engine along with the rotor;
- Turn the rotor with a screwdriver, resting against the notch.
If the cause of the breakdown lies in foreign objects getting into the device, then you need to act in the following order:
- Turn off the power to the pump;
- Drain the water;
- Unscrew the screws holding the motor housing;
- Find and remove foreign objects;
- Install a strainer on the inlet pipe.
Once the repair is complete, the device will start working again. The filtration element will protect the device from solid particles, which will significantly extend the service life of the entire system.